R&D: Hybrid membrane + activated carbon removes hormones from water
German industry collaboration
German researchers have developed a novel way for the energy-efficient removal of steroid hormones from wastewater.
A team at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have combined a polymer membrane together with activated carbon.
The solution has been developed to filter out micropollutants in drinking water, including estrogen steroid hormones, including estradiol.
Due to the low concentration and small size of the molecules, steroid hormones are not only are difficult to detect but can also be difficult to remove, KIT said, adding: “Conventional sewage treatment technologies are not sufficient.”
It was developed with filter manufacturer Blücher GmbH, together with KIT’s Institute of Functional Interfaces, Institute for Applied Materials, and the Karlsruhe Nano Micro Facility.
A wide variety of applications
The researchers believe using the solution it’s possible to reach a limit proposed by the European Commission: 1 nanogram estradiol per litre of drinking water.
Professor Andrea Iris Schäfer, head of KIT’s Institute for Advanced Membrane Technology (IAMT) led the work, which was published in Water Research.
She believes the development has the potential for a wide variety of applications.
“The method allows for a high water flow rate at low pressure, is energy-efficient, and separates many molecules without producing any harmful by-products,” she said. “It can be used flexibly in systems of variable size, from the tap to industrial facilities.”
99 per cent removal achieved
So how does the solution work?
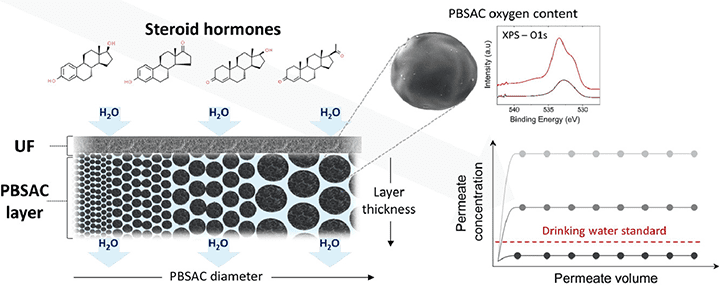
First, water is pressed through a semipermeable membrane that eliminates larger impurities and microorganisms.
Then, water flows through the layer of carbon particles behind, which bind the hormone molecules.
In an activated carbon layer of 2 mm thickness, the researchers decreased the particle diameter from 640 to 80 µm and succeeded in eliminating 96 per cent of the estradiol contained in the water.
The separation efficiency of estradiol of more than 99 per cent was achieved by increasing the oxygen concentration in the activated carbon.
Related content
Share your water technology stories with us
Do you have an innovation, research results or an other interesting topic you would like to share with the international water technology industry? The Aquatech website and social media channels are a great platform to showcase your stories!
Please contact our Sr Brand Marketing Manager Annelie Koomen.
Are you an Aquatech exhibitor?
Make sure you add your latest press releases to your Company Profile in the Exhibitor Portal for free exposure.
We promise never to send you spam and you can unsubscribe at any time!


.jpg?h=628&iar=0&w=1200)
